Hive语法及其进阶(一)
1、Hive完整建表
1 CREATE [EXTERNAL] TABLE [IF NOT EXISTS] table_name( 2 [(col_name data_type [COMMENT col_comment], ...)] 3 ) 4 [COMMENT table_comment]
5 [PARTITIONED BY (col_name data_type [COMMENT col_comment], ...)] 6 [CLUSTERED BY (col_name, col_name, ...) 7 [SORTED BY (col_name [ASC|DESC], ...)] INTO num_buckets BUCKETS] 8 [
9 [ROW FORMAT row_format]
10 [STORED AS file_format]
11 | STORED BY 'storage.handler.class.name' [ WITH SERDEPROPERTIES (...) ] (Note: only available starting with 0.6.0) 12 ] 13 [LOCATION hdfs_path]
14 [TBLPROPERTIES (property_name=property_value, ...)] (Note: only available starting with 0.6.0) 15 [AS select_statement] (Note: this feature is only available starting with 0.5.0.)
注意:
[]:表示可选
EXTERNAL:外部表
(col_name data_type [COMMENT col_comment],...:定义字段名,字段类型
COMMENT col_comment:给字段加上注释
COMMENT table_comment:给表加上注释
PARTITIONED BY (col_name data_type [COMMENT col_comment],...):分区 分区字段注释
CLUSTERED BY (col_name, col_name,...):分桶
SORTED BY (col_name [ASC|DESC], ...)] INTO num_buckets BUCKETS:设置排序字段 升序、降序
ROW FORMAT row_format:指定设置行、列分隔符(默认行分隔符为\n)
STORED AS file_format:指定Hive储存格式:textFile、rcFile、SequenceFile 默认为:textFile
LOCATION hdfs_path:指定储存位置(默认位置在hive.warehouse目录下)
TBLPROPERTIES (property_name=property_value, ...):跟外部表配合使用,比如:映射HBase表,然后可以使用HQL对hbase数据进行查询,当然速度比较慢
AS select_statement:从别的表中加载数据 select_statement=sql语句
2、使用默认方式建表
1 create table students01 2 ( 3 id bigint, 4 name string, 5 age int, 6 gender string, 7 clazz string 8 ) 9 ROW FORMAT DELIMITED FIELDS TERMINATED BY ',';
注意:
分割符不指定,默认不分割
通常指定列分隔符,如果字段只有一列可以不指定分割符:
ROW FORMAT DELIMITED FIELDS TERMINATED BY ',';
3、建表2:指定location
1 create table students02 2 ( 3 id bigint, 4 name string, 5 age int, 6 gender string, 7 clazz string 8 ) 9 ROW FORMAT DELIMITED FIELDS TERMINATED BY ','
10 LOCATION 'data';

4、建表3:指定存储格式
1 create table student_rc 2 ( 3 id bigint, 4 name string, 5 age int, 6 gender string, 7 clazz string 8 ) 9 ROW FORMAT DELIMITED FIELDS TERMINATED BY ','
10 STORED AS rcfile;
注意:
指定储存格式为rcfile,inputFormat:RCFileInputFormat,outputFormat:RCFileOutputFormat,如果不指定,默认为textfile
注意:
除textfile以外,其他的存储格式的数据都不能直接加载,需要使用从表加载的方式。



5、建表4:从其他表中加载数据
格式:
create table xxxx as select_statement(SQL语句) (这种方式比较常用)
例子:
create table students4 as select * from students2;

6、建表5:从其他表中获取表结构
格式:
create table xxxx like table_name 只想建表,不需要加载数据
例子:
create table student04 like students;
7.Hive加载数据
1、使用```hadoop dfs -put '本地数据' 'hive表对应的HDFS目录下

2、使用 load data inpath(是对hdfs的文件移动,移动,移动,不是复制)
3、使用load data local inpath(经常使用,从本地文件中上传)
// overwrite 覆盖加载
// 实际上就是hadoop执行了rmr然后put操作
例如:load data local inpath'/usr/local/data/students.txt' overwrite into table student01;
方式1和方式2的区别:
1.上传数据到hdfs目录和hive表没有任何关系(不需要数据格式进行匹配,hive读取数据还是需要数据格式的匹配)
2.上传数据到hive表和hive表有关系(需要数据格式进行匹配)
8. 清空表
truncate table student01;
注意: 清空代表清空数据,不是删除表
11. insert into table xxxx SQL语句 (没有as) 传输给别的格式的hive table
例如:
insert into table student04 select * from student01;
覆盖插入 把into 换成 overwrite
例如:
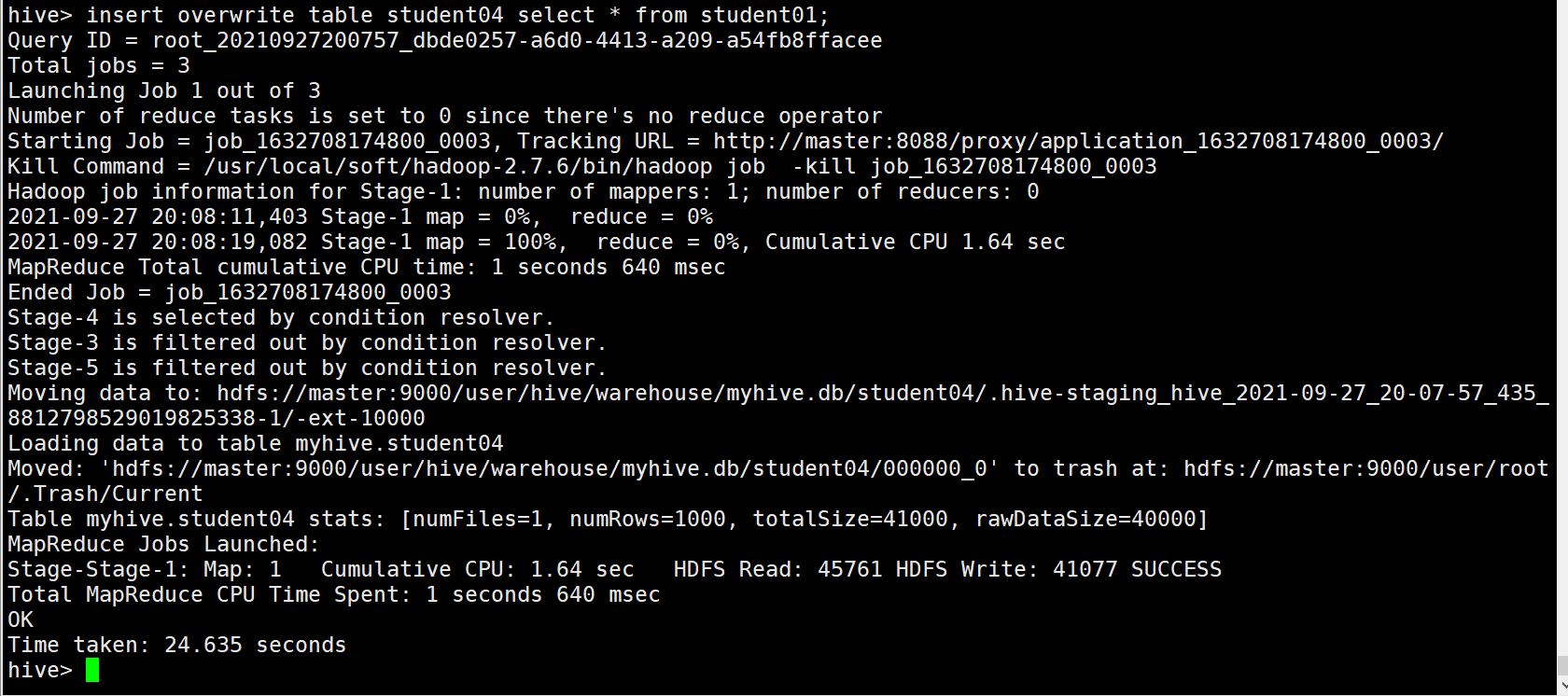
insert overwrite table student04 select * from student01;
9、Hive 内部表(Managed tables)vs 外部表(External tables)
区别:
内部表删除数据跟着删除
外部表只会删除表结构,数据依然存在
注意:
公司中实际应用场景为外部表,为了避免表意外删除数据也丢失
不能通过路径来判断是目录还是hive表(是内部表还是外部表)
建表:
1 内部表 2 create table students_managed01 3 ( 4 id bigint, 5 name string, 6 age int, 7 gender string, 8 clazz string 9 ) 10 ROW FORMAT DELIMITED FIELDS TERMINATED BY ',';

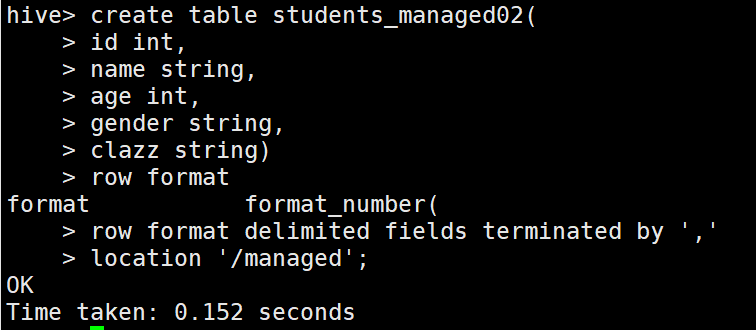
1 //内部表指定location 2 create table students_managed02 3 ( 4 id bigint, 5 name string, 6 age int, 7 gender string, 8 clazz string 9 ) 10 ROW FORMAT DELIMITED FIELDS TERMINATED BY ','
11 LOCATION '/managed';
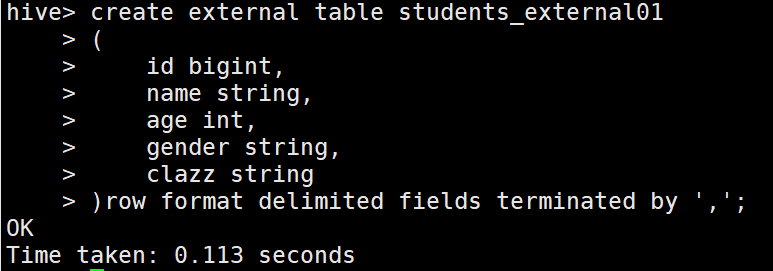
1 // 外部表 2 create external table students_external01 3 ( 4 id bigint, 5 name string, 6 age int, 7 gender string, 8 clazz string 9 ) 10 ROW FORMAT DELIMITED FIELDS TERMINATED BY ',';
1 // 外部表指定location 2 create external table students_external02 3 ( 4 id bigint, 5 name string, 6 age int, 7 gender string, 8 clazz string 9 ) 10 ROW FORMAT DELIMITED FIELDS TERMINATED BY ','; 11 LOCATION '/external';

上传数据:
hive> load data local inpath '/usr/local/data/students.txt'into table students_managed01;hive> load data local inpath '/usr/local/data/students.txt'into table students_managed02;
hive> load data local inpath '/usr/local/data/students.txt'into table students_external01;hive> load data local inpath '/usr/local/data/students.txt'into table students_external02;

删除数据:
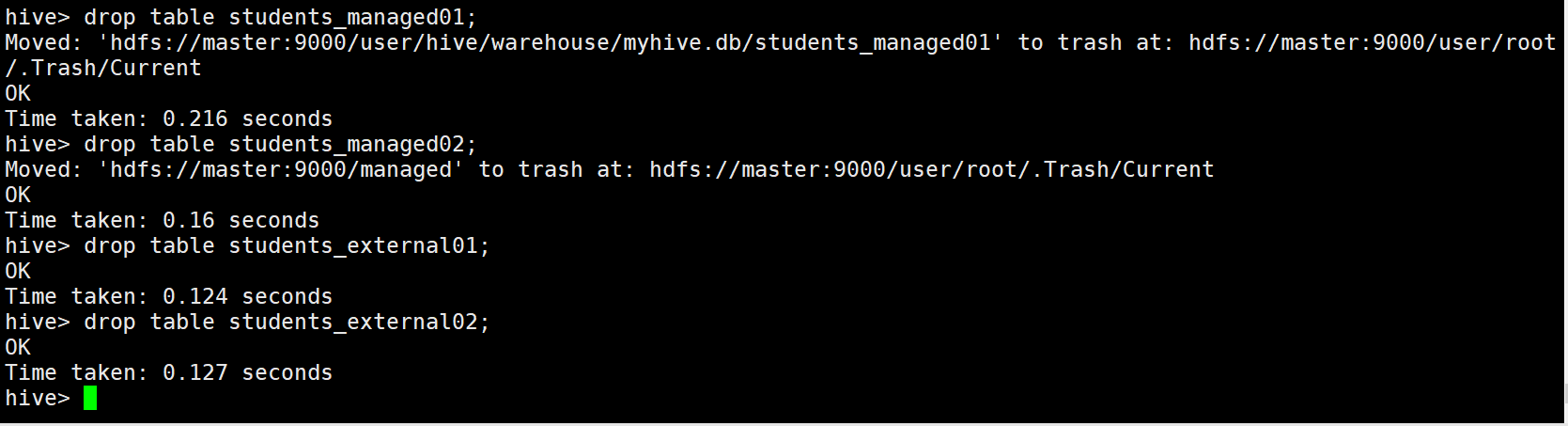
hive> drop table students_managed01; hive> drop table students_managed02; hive> drop table students_external01; hive> drop table students_external02;
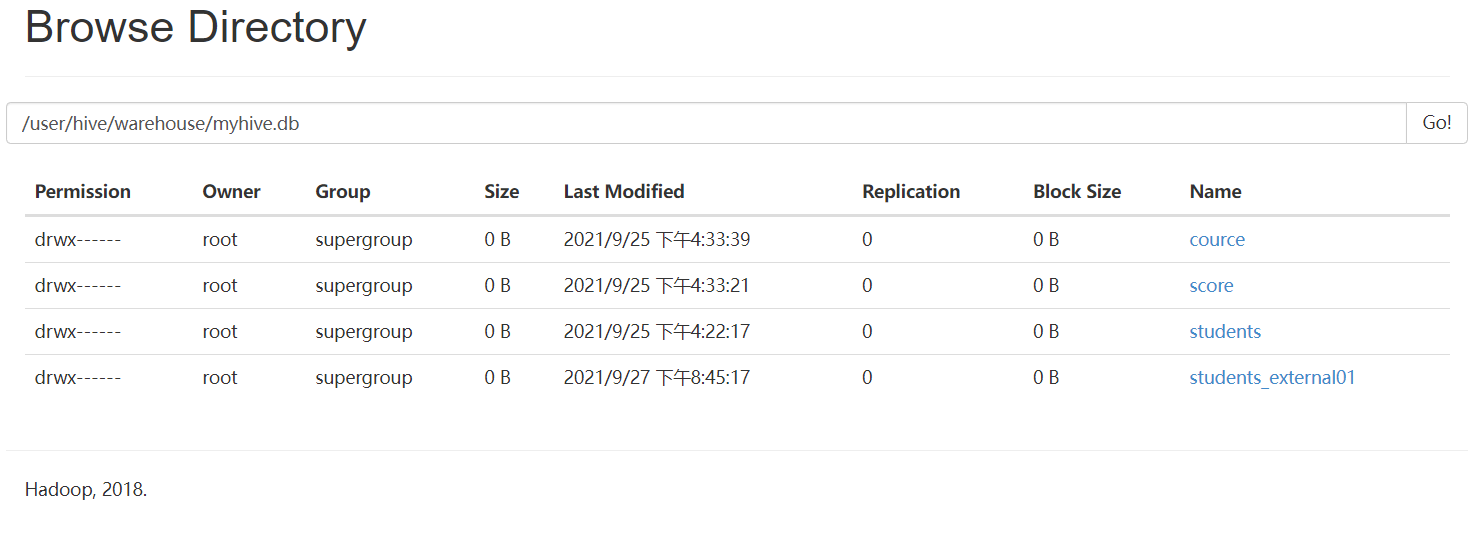
外部表与内部表总结:
可以看出,删除内部表的时候,表中的数据(HDFS上的文件)会被同表的元数据一起删除
删除外部表的时候,只会删除表的元数据,不会删除表中的数据(HDFS上的文件)
一般在公司中,使用外部表多一点,因为数据可以需要被多个程序使用,避免误删,通常外部表会结合location一起使用
外部表还可以将其他数据源中的数据 映射到 hive中,比如说:hbase,ElasticSearch......
设计外部表的初衷就是 让 表的元数据 与 数据 解耦
10、Hive建立单级分区表
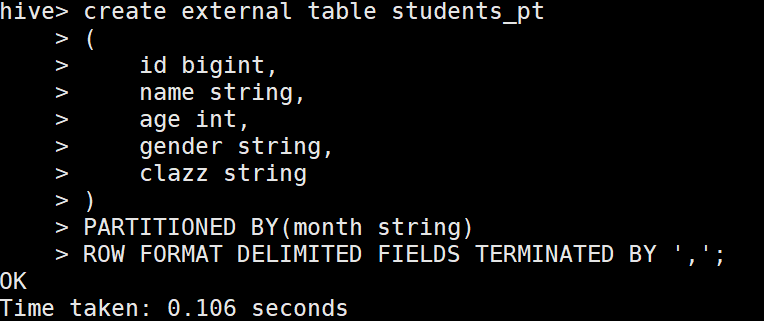
1.创建单级分区
1 create table students_pt 2 ( 3 id bigint, 4 name string, 5 age int, 6 gender string, 7 clazz string 8 ) 9 PARTITIONED BY(month string) 10 ROW FORMAT DELIMITED FIELDS TERMINATED BY ',';
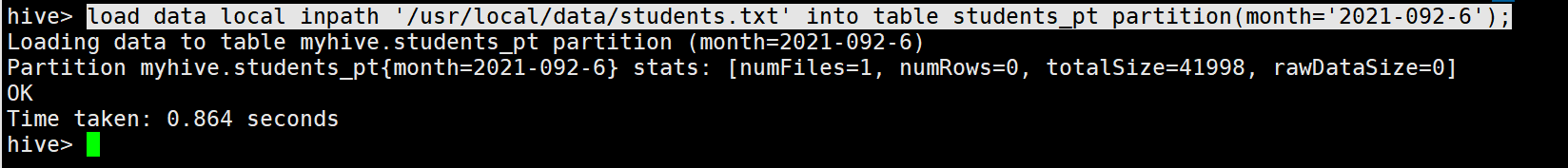
2.加载数据
load data local inpath '/usr/local/data/students.txt' into table students_pt partition(month='2021-09-26');
3.分区查询
单分区查询
select * from students_pt where month='2021-09-26';
多分区查询
select * from students_pt where month='2021-09-26'or month='2021-09-24';
4.增加分区
创建单个分区
alter table students_pt add partition(month='2021-09-25');

创建多个分区
alter table students_pt add partition(month='2021-09-23') partition(month='2021-09-24');(注意中间没有逗号分割)

5.删除分区
删除单个分区
alter table students_pt drop partition(month='2021-09-23');
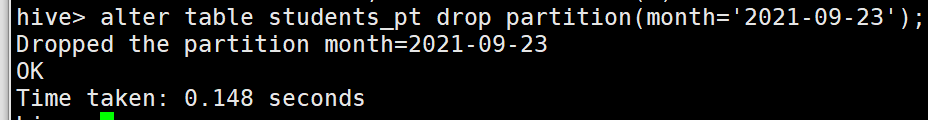
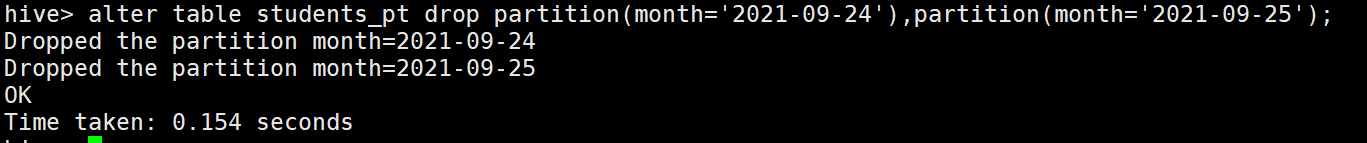
删除多个分区
alter table students_pt drop partition(month='2021-09-24'),partition(month='2021-09-25'); (注意中间有逗号分割)
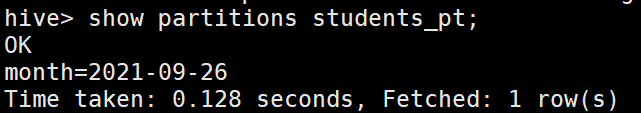
6.查看分区表分区
show partitions students_pt;
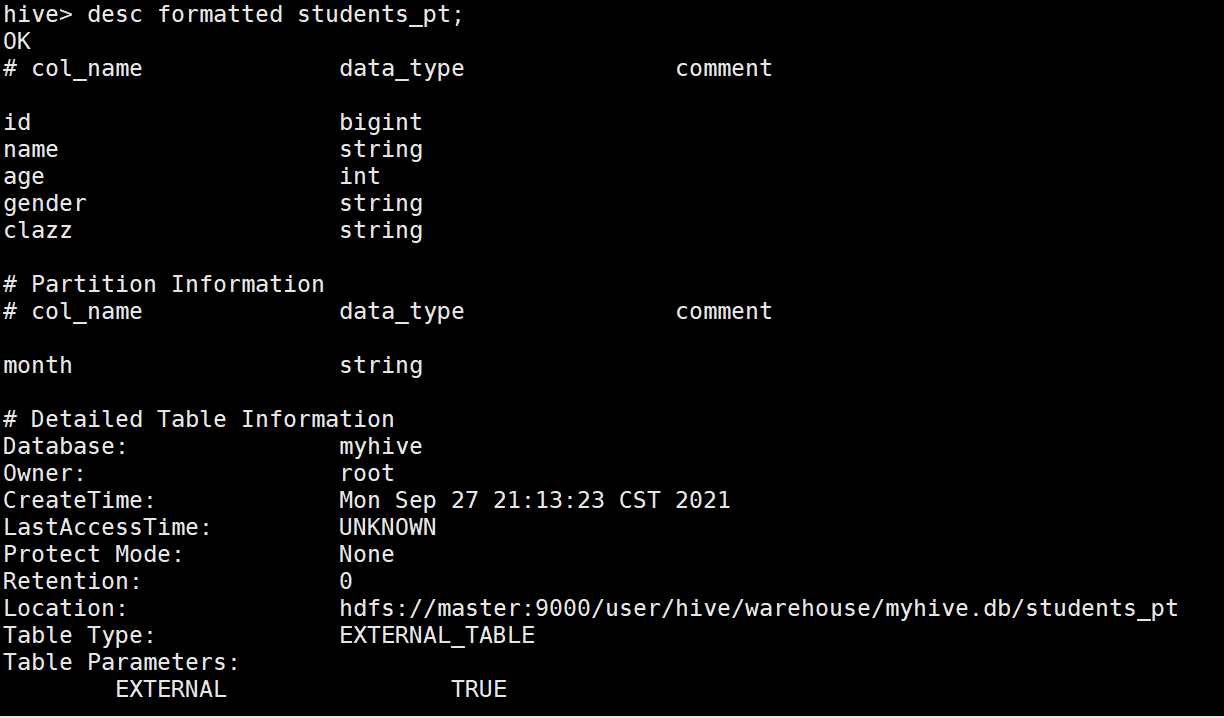
7.查看分区表结构
desc formatted students_pt;
11、Hive建立多级分区表
1.创建二级分区表
1 hive> create table score_pt( 2 > id int, 3 > subjectid int, 4 > score int) 5 > partitioned by (month string,day string) 6 > row format delimited fields terminated by ',';

2.上传数据
1 load data local inpath '/usr/local/data/score.txt' into table score_pt partition(month='2021-09',day='01')

3.加载数据
1 select * from score_pt where month='2021-09' and day='01';
4.添加二级分区
1 hive> alter table score_pt add partition(month='2021-09',day=02);

1 alter table score_pt add partition(month='2021-09',day=03) partition(month='2021-09',day=04);
注意:没有逗号,和添加单级分区一样
5.删除二级分区
1 alter table score_pt drop partition(month='2021-09',day=02);

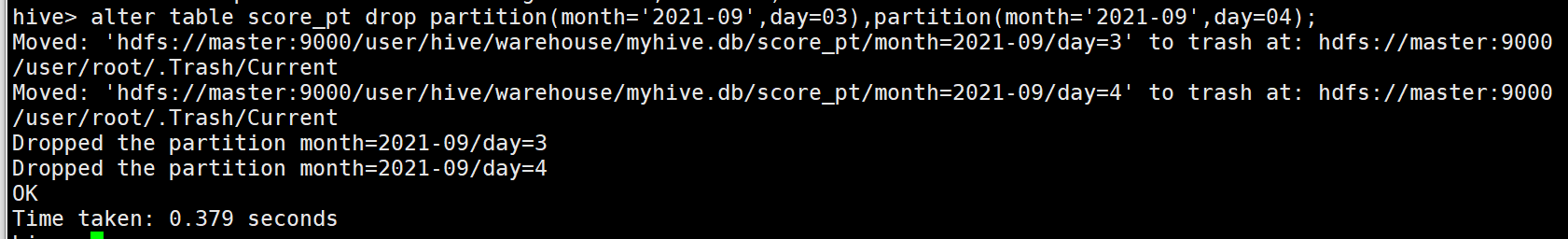
1 alter table score_pt drop partition(month='2021-09',day=03),partition(month='2021-09',day=04);
注意:有逗号,和删除单级分区一样
12.动态分区
> 有的时候我们原始表中的数据里面包含了 ''日期字段 dt'',我们需要根据dt中不同的日期,分为不同的分区,将原始表改造成分区表。
>
> hive默认不开启动态分区
>
> 动态分区:根据数据中某几列的不同的取值 划分 不同的分区
##### 开启Hive的动态分区支持
```
# 表示开启动态分区
hive> set hive.exec.dynamic.partition=true;
# 表示动态分区模式:strict(需要配合静态分区一起使用)、nostrict
# strict: insert into table students_pt partition(dt='anhui',pt) select ......,pt from students;
hive> set hive.exec.dynamic.partition.mode=nostrict;
# 表示支持的最大的分区数量为1000,可以根据业务自己调整
hive> set hive.exec.max.dynamic.partitions.pernode=1000;
#### 使用动态分区插入数据
1.创建表
存储数据
1 create table students_dt 2 ( 3 id bigint, 4 name string, 5 age int, 6 gender string, 7 clazz string, 8 dt string 9 ) 10 ROW FORMAT DELIMITED FIELDS TERMINATED BY ',';
1 create table students_dt_p 2 ( 3 id bigint, 4 name string, 5 age int, 6 gender string, 7 clazz string 8 ) 9 PARTITIONED BY(dt string) 10 ROW FORMAT DELIMITED FIELDS TERMINATED BY ',';
2.插入数据(只能用这一种方式)
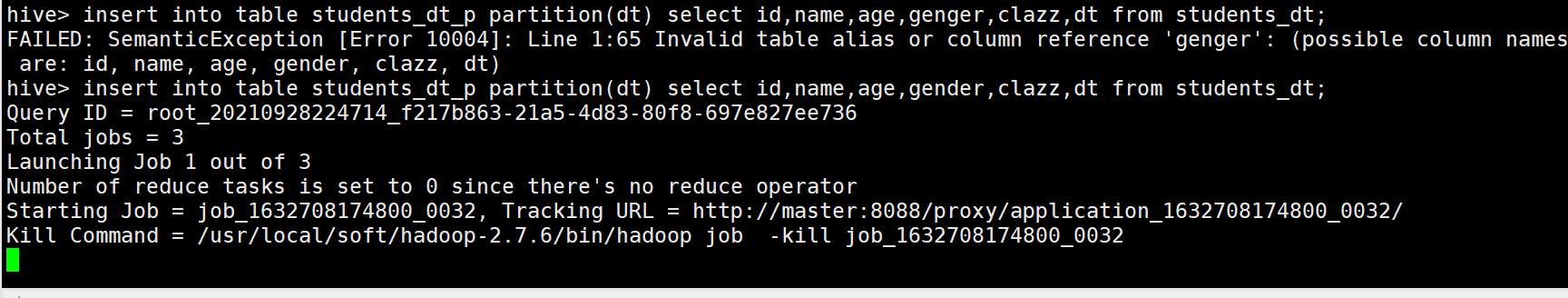
// 分区字段需要放在 select 的最后,如果有多个分区字段 同理,它是按位置匹配,不是按名字匹配
insert into table students_dt_p partition(dt) select id,name,age,gender,clazz,dt from students_dt;

上单讲分区:https://developer.aliyun.com/article/81775
#### Hive分桶
> 分桶实际上是对文件(数据)的进一步切分
>
> Hive默认关闭分桶
>
> 作用:在往分桶表中插入数据的时候,会根据 clustered by 指定的字段 进行hash分区 对指定的buckets个数 进行取余,进而可以将数据分割成buckets个数个文件,以达到数据均匀分布,可以解决Map端的“数据倾斜”问题,方便我们取抽样数据,提高Map join效率
>
> 分桶字段 需要根据业务进行设定
##### 开启分桶开关
```
hive> set hive.enforce.bucketing=true;
```
##### 建立分桶表
create table students_buks
(
id bigint,
name string,
age int,
gender string,
clazz string
)
CLUSTERED BY (clazz) into 12 BUCKETS
ROW FORMAT DELIMITED FIELDS TERMINATED BY ',';
```
##### 往分桶表中插入数据
```
// 直接使用load data 并不能将数据打散
load data local inpath '/usr/local/soft/data/students.txt' into table students_buks;
// 需要使用下面这种方式插入数据,才能使分桶表真正发挥作用
insert into students_buks select * from students;
目录 返回
首页