Linux下的Mongodb部署应用梳理
一、Mongodb简介 官网地址:http://www.mongodb.org/
MongoDB是一个高性能,开源,无模式的文档型数据库,是当前NoSql数据库中比较热门的一种。MongoDB 是一个介于关系数据库和非关系数据库之间的产品,是非关系数据库当中功能 最丰富,最像关系数据库的。它在许多场景下可用于替代传统的关系型数据库或键/值存储方式。它是由C++语言编写的一个基于分布式文件存储的开源数据库系统,它的目的在于为WEB应 用提供可扩展的高性能数据存储解决方案。MongoDB是一个介于关系型数据库和非关系型数据库之间的产品,是非关系型数据库当中功能最丰富,最像关系型数据库的。它支持的数据结构 非常松散,会将数据存储为一个文档,数据结构由键值对(key=>value)组成,是类似于json的bson格式,字段值可以包含其它文档、数组和文档数组,因此可以存储比较复杂的数据类型。
二、Mongodb特点
MongoDB特点是高性能、易部署、易使用,存储数据非常方便,最大的特点在于它支持的查询语言非常强大,其语法有点类似于面向对象的查询语言,几乎可以实现类似关系型数据库单表 查询的绝大部分功能,而且还支持对数据建立索引。MongoDB的主要特点总结如下: 1)提供了一个面向集合的文档存储,易存储对象类型的数据,操作起来比较简单和容易的非关系型数据库 2)使用update()命令可以实现替换完成的文档(数据)或者一些指定的数据字段。 3)支持动态查询。 4)支持完全索引,包含内部对象,可以在MongoDB记录中设置任何属性的索引来实现更快的排序。 5)支持复制和故障恢复。 6)使用高效的二进制数据存储,包括大型对象(如视频等)。 7)GridFS是MongoDB中的一个内置功能,可以用于存放大量小文件。 8)自动处理碎片,以支持云计算层次的扩展性;如果负载的增加(需要更多的存储空间和更强的处理能力),它可以分布在计算机网络中的其它节点上,这就是所谓的分片。 9)支持RUBY,PYTHON,JAVA,C++,PHP,C#等多种语言。 10)文件存储格式为BSON(一种JSON的扩展),MongoDB支持丰富的查询表达式,查询指令使用JSON形式的标记,可轻易查询文档中内嵌的对象和数组。 11)MongoDB允许在服务端执行脚本,可以用JavaScript编写某个函数,直接在服务端执行,也可以吧函数的定义存储在服务端,下次直接调用即可。 12)可通过网络访问,可以通过本地u或者网络创建数据镜像,这使得MongoDB含有更强的扩展性。
Mongodb的不足之处
1)在集群分片中的数据分布不均匀
2)单机可靠性比较差
3)大数据量持续插入,写入性能有较大波动
4)不支持事务操作。所以事务要求严格的系统(如果银行系统)肯定不能用它。
5)磁盘空间占用比较大。空间占用大的原因如下:
1-> 空间的预分配:为避免形成过多的硬盘碎片,mongodb 每次空间不足时都会申请生成一大块的硬盘空 间,而且申请的量从 64M、128M、256M 那样的指数递增,直到2G为单个文件
的最大体积。随着数据量 的增加,你可以在其数据目录里看到这些整块生成容量不断递增的文件。
2-> 字段名所占用的空间:为了保持每个记录内的结构信息用于查询,mongodb 需要把每个字段的 key-value 都以 BSON 的形式存储,如果 value 域相对于 key 域并不大,比如
存放数值型的数据,则数据的 overhead 是最大的。一种减少空间占用的方法是把字段名尽量取短一些,这样占用 空间就小了,但这就要求在易读 性与空间占用上作为权衡了。
3-> 删除记录不释放空间:这很容易理解,为避免记录删除后的数据的大规模挪动,原记录空间不删除,只 标记“已删除”即可,以后还可以重复利用。
4-> 可以定期运行 db.repairDatabase()来整理记录,但这个过程会比较缓慢
三、Mongodb功能
1)面向集合的存储:适合存储对象及JSON形式的数据。 2)动态查询:Mongo支持丰富的查询表达式。查询指令使用JSON形式的标记,可轻易查询文档中内嵌的对象及数组。 3)完整的索引支持:包括文档内嵌对象及数组。Mongo的查询优化器会分析查询表达式,并生成一个高效的查询计划。 4)查询监视:Mongo包含一个监视工具用于分析数据库操作的性能。 5)复制及自动故障转移:Mongo数据库支持服务器之间的数据复制,支持主-从模式及服务器之间的相互复制。复制的主要目标是提供冗余及自动故障转移。 6)高效的传统存储方式:支持二进制数据及大型对象(如照片或图片) 7)自动分片以支持云级别的伸缩性:自动分片功能支持水平的数据库集群,可动态添加额外的机器。
四、Mongodb使用场景
适用场景: 网站实时数据处理。它非常适合实时的插入、更新与查询,并具备网站实时数据存储所需的复制及高度伸缩性;缓存,由于性能很高,它适合作为信息基础设施的缓存层。在系统重启之后, 由它搭建的持久化缓存层可以避免下层的数据源过载。高伸缩性的场景。非常适合由数十或数百台服务器组成的数据库,它的路线图中已经包含对MapReduce引擎的内置支持。 不适用场景: 要求高度事务性的系统。传统的商业智能应用。复杂的跨文档(表)级联查询。
五、Mongodb安装使用 官网下载地址:http://www.mongodb.org/downloads
1)安装mongodb
[root@data-server src]# cd /usr/local/src/
[root@data-server src]# tar -zvxf mongodb-linux-x86_64-rhel62-3.4.4
[root@data-server src]# mv mongodb-linux-x86_64-rhel62-3.4.4 /usr/local/mongodb
[root@data-server src]# cd /usr/local/mongodb //Mongodb主目录
[root@data-server mongodb]# ll
总用量 120
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 4096 6月 3 14:51 bin
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 34520 4月 21 06:19 GNU-AGPL-3.0
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 16726 4月 21 06:19 MPL-2
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 1359 4月 21 06:19 README
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 55625 4月 21 06:19 THIRD-PARTY-NOTICES
[root@data-server mongodb]# mkdir /usr/local/mongodb/data //Mongodb数据目录,可以存放在一个独立的大分区上
[root@data-server mongodb]# mkdir /usr/local/mongodb/log //Mongodb日志目录
2)启动Mongodb
使用mongod命令建立一个mongodb数据库链接,端口号设置为10001,数据库的路径为/usr/local/mongodb/data,日志路径为/usr/local/mongodb/log/mongo.log
mongodb的启动程序放在后台执行,下面命令执行后,按ctrl+c
[root@data-server mongodb]# nohup /usr/local/mongodb/bin/mongod --dbpath=/usr/local/mongodb/data/ --logpath=/usr/local/mongodb/log/mongo.log &
mongodb默认端口是27017
[root@data-server mongodb]# ps -ef|grep mongodb
root 14858 14518 1 15:01 pts/1 00:00:01 /usr/local/mongodb/bin/mongod --dbpath=/usr/local/mongodb/data/ --logpath=/usr/local/mongodb/log/mongo.log
root 14887 14518 0 15:02 pts/1 00:00:00 grep mongodb
[root@data-server bin]# netstat -tunlp|grep 14858
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:27017 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 14858/mongod
[root@data-server mongodb]# lsof -i:27017
COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME
mongod 14858 root 7u IPv4 145311 0t0 TCP *:27017 (LISTEN)
3)设置mongodb的环境变量
[root@data-server ~]# vim /etc/profile
.......
export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/mongodb/bin/
[root@data-server ~]# source /etc/profile
4)为了更方便的启动和关闭MongoDB,我们可以使用Shell写脚本,当然也可以加入到service中
更好的方式是采用配置文件,把MongoDB需要的参数写入配置文件,然后在脚本中引用;
[root@data-server ~]# cat /usr/local/mongodb/mongodb.conf
#代表端口号,如果不指定则默认为27017
port=27017
#MongoDB数据文件目录
dbpath=/usr/local/mongodb/data
#MongoDB日志文件目录
logpath=/usr/local/mongodb/log/mongo.log
#日志文件自动累加
logappend=true
编写启动脚本
[root@data-server ~]# vim /etc/init.d/mongodb
#!/bin/bash
#
# mongod Start up the MongoDB server daemon
#
# source function library
. /etc/rc.d/init.d/functions
#定义命令
CMD=/usr/local/mongodb/bin/mongod
#定义配置文件路径
INITFILE=/usr/local/mongodb/mongodb.conf
start()
{
#&表示后台启动,也可以使用fork参数
$CMD -f $INITFILE &
echo "MongoDB is running background..."
}
stop()
{
pkill mongod
echo "MongoDB is stopped."
}
case "$1" in
start)
start
;;
stop)
stop
;;
*)
echo $"Usage: $0 {start|stop}"
esac
[root@data-server ~]# chmod 755 /etc/init.d/mongodb
[root@data-server ~]# /etc/init.d/mongodb status
用法:/etc/init.d/mongodb {start|stop}
[root@data-server ~]# /etc/init.d/mongodb stop
已终止
[root@data-server ~]# lsof -i:27017
[root@data-server ~]# /etc/init.d/mongodb start
MongoDB is running background...
[root@data-server ~]# lsof -i:27017
COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME
mongod 15138 root 7u IPv4 147713 0t0 TCP *:27017 (LISTEN)
通过 shell 连接 MongoDB 服务:(在客户机上连接本机mongodb:mongo 182.48.115.238:27017)
[root@data-server ~]# mongo
MongoDB shell version v3.4.4
connecting to: mongodb://127.0.0.1:27017
MongoDB server version: 3.4.4
Welcome to the MongoDB shell.
For interactive help, type "help".
For more comprehensive documentation, see
http://docs.mongodb.org/
Questions? Try the support group
http://groups.google.com/group/mongodb-user
Server has startup warnings:
2017-06-03T15:17:54.695+0800 I STORAGE [initandlisten]
2017-06-03T15:17:54.695+0800 I STORAGE [initandlisten] ** WARNING: Using the XFS filesystem is strongly recommended with the WiredTiger storage engine
2017-06-03T15:17:54.695+0800 I STORAGE [initandlisten] ** See http://dochub.mongodb.org/core/prodnotes-filesystem
2017-06-03T15:17:55.699+0800 I CONTROL [initandlisten]
2017-06-03T15:17:55.700+0800 I CONTROL [initandlisten] ** WARNING: Access control is not enabled for the database.
2017-06-03T15:17:55.700+0800 I CONTROL [initandlisten] ** Read and write access to data and configuration is unrestricted.
2017-06-03T15:17:55.700+0800 I CONTROL [initandlisten] ** WARNING: You are running this process as the root user, which is not recommended.
2017-06-03T15:17:55.700+0800 I CONTROL [initandlisten]
2017-06-03T15:17:55.700+0800 I CONTROL [initandlisten]
2017-06-03T15:17:55.700+0800 I CONTROL [initandlisten] ** WARNING: /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/enabled is 'always'.
2017-06-03T15:17:55.700+0800 I CONTROL [initandlisten] ** We suggest setting it to 'never'
2017-06-03T15:17:55.700+0800 I CONTROL [initandlisten]
2017-06-03T15:17:55.700+0800 I CONTROL [initandlisten] ** WARNING: /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/defrag is 'always'.
2017-06-03T15:17:55.700+0800 I CONTROL [initandlisten] ** We suggest setting it to 'never'
2017-06-03T15:17:55.700+0800 I CONTROL [initandlisten]
> help
db.help() help on db methods
db.mycoll.help() help on collection methods
sh.help() sharding helpers
rs.help() replica set helpers
help admin administrative help
help connect connecting to a db help
help keys key shortcuts
help misc misc things to know
help mr mapreduce
show dbs show database names
show collections show collections in current database
show users show users in current database
show profile show most recent system.profile entries with time >= 1ms
show logs show the accessible logger names
show log [name] prints out the last segment of log in memory, 'global' is default
use <db_name> set current database
db.foo.find() list objects in collection foo
db.foo.find( { a : 1 } ) list objects in foo where a == 1
it result of the last line evaluated; use to further iterate
DBQuery.shellBatchSize = x set default number of items to display on shell
exit quit the mongo shell
mongodb非正常关闭导致启动失败问题
之前强制关闭了mongodb,后续再次启动的时候,发现报错:
[root@i-omxpbsuo ~]# /usr/local/mongodb/bin/mongod --logpath /usr/local/mongodb/log/system.log --logappend --dbpath /data/mongodb --directoryperdb --auth --journal --profile=1 --slowms=5 --fork
forked process: 4853
all output going to: /usr/local/mongodb/log/system.log
查看日志
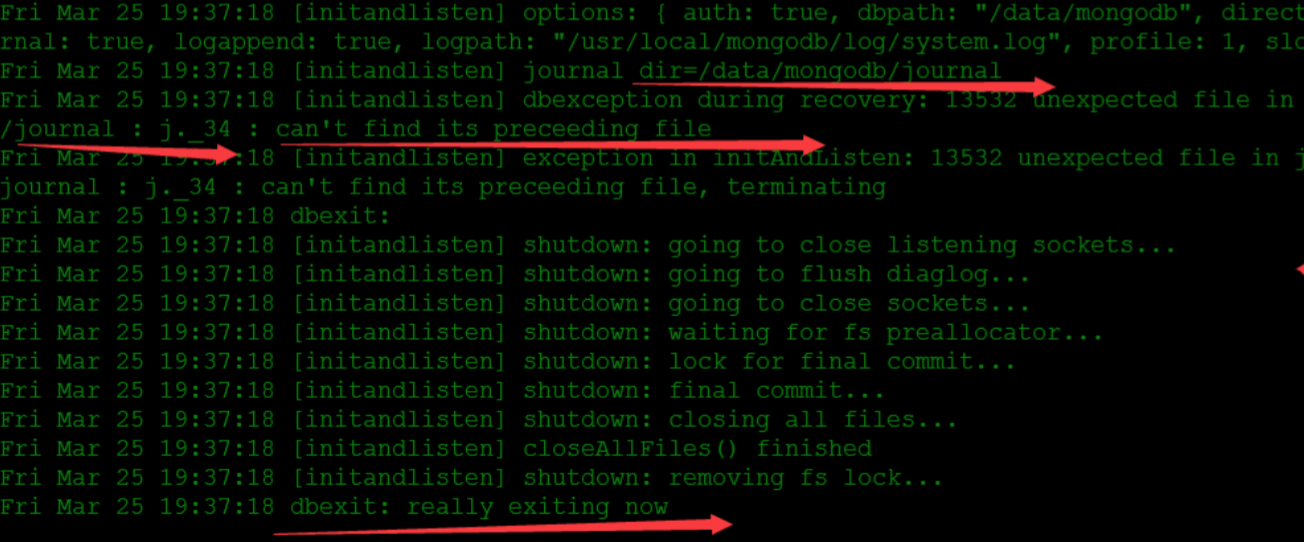
这是由于上次mongodb非正常关闭导致的。
解决办法:
1)删除数据目录/data/mongodb 下的 mongod.lock
[root@i-omxpbsuo ~]# rm -rf /data/mongodb/mongod.lock
2)修复mongodb
[root@i-omxpbsuo ~]# /usr/local/mongodb/bin/mongod --logpath --dbpath /data/mongodb --repair
3)删除/data/mongodb/journal 下的 j._4 文件(或者将journal下的文件清空)
[root@i-omxpbsuo ~]# rm -rf /data/mongodb/journal/*j._4
4)然后再次启动mongodb就ok了
[root@i-omxpbsuo ~]# /usr/local/mongodb/bin/mongod --logpath --dbpath /data/mongodb --directoryperdb --auth --journal --profile=1 --slowms=5 --fork &
======================================================== 正确关闭mongod 的方法:进入mongo shell > use admin > db.shutdownServer() 也可以按照文档粗暴的杀掉它,它内部应该有KILL信号处理程序。 # killall mongod 请不要 kill -9 ,会造成文件数据混乱丢失repair也无力回天。 =======================================================
除此之外,还可以采用yum的方式安装mongodb,操作记录如下:
1)创建repo
[root@data-server ~]# vim /etc/yum.repos.d/mongodb-org-3.2.repo
[mongodb-org-3.2]
name=MongoDB Repository
baseurl=https://repo.mongodb.org/yum/redhat/$releasever/mongodb-org/3.2/x86_64/
gpgcheck=0
enabled=1
2)安装MongoDB和相关工具
[root@data-server ~]# yum install -y mongodb-org
3)启动Mongodb
[root@data-server ~]# service mongod start
Starting mongod: [ OK ]
[root@data-server ~]# chkconfig mongod on
[root@data-server ~]# lsof -i:27017
COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME
mongod 26130 mongod 6u IPv4 2773161 0t0 TCP localhost:27017 (LISTEN)
日志文件:/var/log/mongodb/mongod.log
配置文件:/etc/mongod.conf
数据目录:/var/lib/mongo/
配置文件解释:
[root@data-server ~]# cat /etc/mongod.conf
# mongo.conf
#where to log
logpath=/var/log/mongo/mongod.log
logappend=true #以追加方式写入日志
# fork and run in background
fork = true
#port = 27017 #端口
dbpath=/var/lib/mongo #数据库文件保存位置
directoryperdb=true
# Enables periodic logging of CPU utilization and I/O wait
#启用定期记录CPU利用率和 I/O 等待
#cpu = true
# Turn on/off security. Off is currently the default
# 是否以安全认证方式运行,默认是不认证的非安全方式
#noauth = true
#auth = true
# Verbose logging output.
# 详细记录输出
#verbose = true
# Inspect all client data for validity on receipt (useful for
# developing drivers)用于开发驱动程序时的检查客户端接收数据的有效性
#objcheck = true
# Enable db quota management 启用数据库配额管理,默认每个db可以有8个文件,可以用quotaFiles参数设置
#quota = true
# 设置oplog记录等级
# Set oplogging level where n is
# 0=off (default)
# 1=W
# 2=R
# 3=both
# 7=W+some reads
#oplog = 0
# Diagnostic/debugging option 动态调试项
#nocursors = true
# Ignore query hints 忽略查询提示
#nohints = true
# 禁用http界面,默认为localhost:28017
# Disable the HTTP interface (Defaults to localhost:27018).这个端口号写的是错的
#nohttpinterface = true
# 关闭服务器端脚本,这将极大的限制功能
# Turns off server-side scripting. This will result in greatly limited
# functionality
#noscripting = true
# 关闭扫描表,任何查询将会是扫描失败
# Turns off table scans. Any query that would do a table scan fails.
#notablescan = true
# 关闭数据文件预分配
# Disable data file preallocation.
#noprealloc = true
# 为新数据库指定.ns文件的大小,单位:MB
# Specify .ns file size for new databases.
# nssize = <size>
# Accout token for Mongo monitoring server.
#mms-token = <token>
# mongo监控服务器的名称
# Server name for Mongo monitoring server.
#mms-name = <server-name>
# mongo监控服务器的ping 间隔
# Ping interval for Mongo monitoring server.
#mms-interval = <seconds>
# Replication Options 复制选项
# in replicated mongo databases, specify here whether this is a slave or master 在复制中,指定当前是从属关系
#slave = true
#source = master.example.com
# Slave only: specify a single database to replicate
#only = master.example.com
# or
#master = true
#source = slave.example.com
六、Mongodb的日常操作命令
1)登陆和退出..........................................
mongo 命令直接加MongoDB服务器的IP地址就可以利用 Mongo 的默认端口号(27017)登陆 Mongo,然后便能够进行简单的命令行操作。至于退出,直接 exit,然后回车就好了。
如果默认bind绑定的ip是127.0.0.1以及端口是27017,那么登陆可以直接用下面两种都可以:
[root@master-node ~]# mongo
[root@master-node ~]# mongo 127.0.0.1:27017
如果是绑定了固定的ip地址,如bind_ip=182.48.115.236,那么连接mongodb命令是:
[root@master-node ~]# mongo 182.48.115.238:27017
如果是连接某个库,命令是
[root@master-node ~]# mongo ip:port/库名 -u用户名 -p密码
> help
登陆mongodb数据库后,可以直接执行help命令进行帮助查看
> show collections
从以上可以看出,登录后 mongo 会自动连上一个名为 test 的数据库。如果这个数据库不存 在,那么 mongo 会自动建立一个名为 test 的数据库。上面的例子,由于 Mongo 服务器上没 有名为 test 的 db,因此,mongo 新建了一个空的名为 test 的 db。其中,没有任何 collection。
2)database级操作..........................................
2.1 查看服务器上的数据库
> show dbs
admin 0.000GB
local 0.000GB
master_slave 0.000GB
wangshibo 0.000GB
2.2 切换数据库
切换到wangshibo数据库(从默认的 test 数据库)
> use wangshibo;
switched to db wangshibo;
mongo 中,db 代表当前使用的数据库。这样,db 就从原来的 test,变为现在的 wangshibo 数据库,如果没有这个库,就会自动创建
2.3 查看当前数据库中的所有集合
> show collections
persons
test
2.4 创建数据库
mongo 中创建数据库采用的也是 use 命令,如果 use 后面跟的数据库名不存在,那么 mongo 将会新建该数据库。
不过,实际上只执行 use 命令后,mongo 是不会新建该数据库的,直到 你像该数据库中插入了数据。
> use huanqiu
switched to db huanqiu
> show dbs
admin 0.000GB
local 0.000GB
master_slave 0.000GB
wangshibo 0.000GB
到这里并没有看到刚才新建的 huanqiu 数据库。
> db.huanqiu.insert({"name":"testdb"})
WriteResult({ "nInserted" : 1 })
该操作会在 huanqiu 数据库中新建一个 hello 集合,并在其中插入一条记录。
> show dbs
admin 0.000GB
huanqiu 0.000GB
local 0.000GB
master_slave 0.000GB
wangshibo 0.000GB
这样,便可以看到 mongo 的确创建了 huanqiu 数据库,其中有一个 hello 集合。
2.5 删除数据库
删除当前所在库。比如这里已经切换到huanqiu库,那么就删除huanku库
> db.dropDatabase()
{ "dropped" : "huanqiu", "ok" : 1 }
> show dbs
admin 0.000GB
local 0.000GB
master_slave 0.000GB
wangshibo 0.000GB
2.6 查看当前数据库
> db
huanqiu
> db.getName(); //这个上面的命令是一样的
wangshibo
可以看出删除 huanqiu 数据库之后,当前的 db 还是指向它,只有当切换数据库之后,huanqiu 才会彻底消失。
> use wangshibo
switched to db wangshibo
> db
wangshibo
> show dbs
admin 0.000GB
local 0.000GB
master_slave 0.000GB
wangshibo 0.000GB
2.6.1 修复当前数据库
> db.repairDatabase();
{ "ok" : 1 }
2.6.2 查看当前数据库状态
> db.stats();
{
"db" : "wangshibo",
"collections" : 3,
"views" : 0,
"objects" : 6,
"avgObjSize" : 75.5,
"dataSize" : 453,
"storageSize" : 73728,
"numExtents" : 0,
"indexes" : 4,
"indexSize" : 53248,
"ok" : 1
}
2.6.3 当前db版本
> db.version();
3.4.4
2.6.4 查看当前db的链接机器地址
> db.getMongo();
connection to 182.48.115.238:27017
2.6.5 从指定主机上克隆数据库
> db.cloneDatabase("182.48.115.236");
{
"clonedColls" : [ ],
"ok" : 0,
"errmsg" : "a collection 'wangshibo.wangshibo' already exists",
"code" : 48,
"codeName" : "NamespaceExists"
}
2.6.6 从指定的机器上复制指定数据库数据到某个数据库
将本机的master_slave的数据复制到wangshibo数据库中
> db.copyDatabase("master_slave", "wangshibo", "127.0.0.1");
{ "ok" : 1 }
3)collection 级操作..........................................
3.1 新建 collection
> db.createCollection("Hello")
{ "ok" : 1 }
> show collections
Hello
wangshibo
直接向一个不存在的 collection 中插入数据也能创建一个 collection。
> db.hello2.insert({"name":"lfqy"})
WriteResult({ "nInserted" : 1 })
> show collections
Hello
hello2
wangshibo
3.2 删除 collection
> db.Hello.drop()
true
返回 true 说明删除成功,false 说明没有删除成功。
> db.Hello.drop()
false
不存在名为 hello 的 collection,因此,删除失败。
3.3 重命名 collection
将 hello2 集合重命名为 HELLO
> show collections
hello2
wangshibo
> db.hello2.renameCollection("HELLO")
{ "ok" : 1 }
> show collections
HELLO
wangshibo
3.4 查看当前数据库中的所有 collection
> show collections
HELLO
wangshibo
3.5 建立索引在 HELLO 集合上,建立对 ID 字段的索引,1 代表升序。
> db.HELLO.ensureIndex({ID:1})
{
"createdCollectionAutomatically" : false,
"numIndexesBefore" : 1,
"numIndexesAfter" : 2,
"ok" : 1
}
4)Record 级的操作................................
4.1 插入操作
4.1.1 向 user 集合中插入两条记录
> db.user.insert({'name':'GalGadot','gender':'female','age':28,'salary':11000})
WriteResult({ "nInserted" : 1 })
> db.user.insert({'name':'Mikie Hara','gender':'female','age':26,'salary':7000})
WriteResult({ "nInserted" : 1 })
4.1.2 同样也可以用 save 完成类似的插入操作
> db.user.save({'name':'Wentworth Earl Miller','gender':'male','age':41,'salary':33000})
WriteResult({ "nInserted" : 1 })
4.2 查找操作
4.2.1 查找集合中的所有记录
> db.user.find()
{ "_id" : ObjectId("59328c8aa7865327915046ae"), "name" : "GalGadot", "gender" : "female", "age" : 28, "salary" : 11000 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("59328c9da7865327915046af"), "name" : "Mikie Hara", "gender" : "female", "age" : 26, "salary" : 7000 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("59328cd6a7865327915046b0"), "name" : "Wentworth Earl Miller", "gender" : "male", "age" : 41, "salary" : 33000 }
4.2.2 查找集合中的符合条件的记录
(1)单一条件
查询 age 为26 的数据
> db.user.find({"age":26})
{ "_id" : ObjectId("59328c9da7865327915046af"), "name" : "Mikie Hara", "gender" : "female", "age" : 26, "salary" : 7000 }
查询 salary 大于 7000 的数据
> db.user.find({salary:{$gt:7000}})
{ "_id" : ObjectId("59328c8aa7865327915046ae"), "name" : "GalGadot", "gender" : "female", "age" : 28, "salary" : 11000 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("59328cd6a7865327915046b0"), "name" : "Wentworth Earl Miller", "gender" : "male", "age" : 41, "salary" : 33000 }
查询 name 中包含'ent'的数据
> db.user.find({name:/ent/})
{ "_id" : ObjectId("59328cd6a7865327915046b0"), "name" : "Wentworth Earl Miller", "gender" : "male", "age" : 41, "salary" : 33000 }
查询 name 以 G 打头的数据
> db.user.find({name:/^G/})
{ "_id" : ObjectId("59328c8aa7865327915046ae"), "name" : "GalGadot", "gender" : "female", "age" : 28, "salary" : 11000 }
查询 name 以 t 结尾的数据
> db.user.find({name:/t$/})
{ "_id" : ObjectId("59328c8aa7865327915046ae"), "name" : "GalGadot", "gender" : "female", "age" : 28, "salary" : 11000 }
(2)多条件"与"
查询 age 小于 30,salary 大于 7000 的数据
> db.user.find({age:{$lt:30},salary:{$gt:7000}})
{ "_id" : ObjectId("59328c8aa7865327915046ae"), "name" : "GalGadot", "gender" : "female", "age" : 28, "salary" : 11000 }
(3)多条件"或"
查询 age 小于 30,或者 salary 大于 10000 的记录
> db.user.find({$or:[{salary:{$gt:10000}},{age:{$lt:30}}]})
{ "_id" : ObjectId("59328c8aa7865327915046ae"), "name" : "GalGadot", "gender" : "female", "age" : 28, "salary" : 11000 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("59328c9da7865327915046af"), "name" : "Mikie Hara", "gender" : "female", "age" : 26, "salary" : 7000 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("59328cd6a7865327915046b0"), "name" : "Wentworth Earl Miller", "gender" : "male", "age" : 41, "salary" : 33000 }
4.2.3 查询第一条记录
将上面的 find 替换为 findOne()可以查找符合条件的第一条记录。
> db.user.findOne({$or:[{salary:{$gt:10000}},{age:{$lt:25}}]})
{
"_id" : ObjectId("59328c8aa7865327915046ae"),
"name" : "GalGadot",
"gender" : "female",
"age" : 28,
"salary" : 11000
}
4.2.4 查询记录的指定字段
查询 user 集合中所有记录的 name,age,salary,sex_orientation 字段
> db.user.find({},{name:1,age:1,salary:1,sex_orientation:true})
{ "_id" : ObjectId("59328c8aa7865327915046ae"), "name" : "GalGadot", "age" : 28, "salary" : 11000 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("59328c9da7865327915046af"), "name" : "Mikie Hara", "age" : 26, "salary" : 7000 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("59328cd6a7865327915046b0"), "name" : "Wentworth Earl Miller", "age" : 41, "salary" : 33000 }
注意:这里的 1 表示显示此列的意思,也可以用 true 表示。
> db.user.find({},{name:1,age:1,salary:true,sex_orientation:1})
{ "_id" : ObjectId("59328c8aa7865327915046ae"), "name" : "GalGadot", "age" : 28, "salary" : 11000 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("59328c9da7865327915046af"), "name" : "Mikie Hara", "age" : 26, "salary" : 7000 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("59328cd6a7865327915046b0"), "name" : "Wentworth Earl Miller", "age" : 41, "salary" : 33000 }
4.2.5 查询指定字段的数据,并去重。
查询 gender 字段的数据,并去掉重复数据
> db.user.distinct('gender')
[ "female", "male" ]
4.2.6 对查询结果集的操作
(1)Pretty Print
为了方便,mongo 也提供了 pretty print 工具,db.collection.pretty()或者是 db.collection.forEach(printjson)
> db.user.find().pretty()
{
"_id" : ObjectId("59328c8aa7865327915046ae"),
"name" : "GalGadot",
"gender" : "female",
"age" : 28,
"salary" : 11000
}
{
"_id" : ObjectId("59328c9da7865327915046af"),
"name" : "Mikie Hara",
"gender" : "female",
"age" : 26,
"salary" : 7000
}
{
"_id" : ObjectId("59328cd6a7865327915046b0"),
"name" : "Wentworth Earl Miller",
"gender" : "male",
"age" : 41,
"salary" : 33000
}
(2)指定结果集显示的条目
a)显示结果集中的前 3 条记录
> db.user.find().limit(3)
{ "_id" : ObjectId("59328c8aa7865327915046ae"), "name" : "GalGadot", "gender" : "female", "age" : 28, "salary" : 11000 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("59328c9da7865327915046af"), "name" : "Mikie Hara", "gender" : "female", "age" : 26, "salary" : 7000 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("59328cd6a7865327915046b0"), "name" : "Wentworth Earl Miller", "gender" : "male", "age" : 41, "salary" : 33000 }
b)查询第 1 条以后的所有数据
> db.user.find().skip(1)
{ "_id" : ObjectId("59328c9da7865327915046af"), "name" : "Mikie Hara", "gender" : "female", "age" : 26, "salary" : 7000 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("59328cd6a7865327915046b0"), "name" : "Wentworth Earl Miller", "gender" : "male", "age" : 41, "salary" : 33000 }
查询跳过前2条以后的所有数据
> db.user.find().skip(2)
{ "_id" : ObjectId("59328cd6a7865327915046b0"), "name" : "Wentworth Earl Miller", "gender" : "male", "age" : 41, "salary" : 33000 }
>
c)对结果集排序
升序
> db.user.find().sort({salary:1})
{ "_id" : ObjectId("59328c9da7865327915046af"), "name" : "Mikie Hara", "gender" : "female", "age" : 26, "salary" : 7000 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("59328c8aa7865327915046ae"), "name" : "GalGadot", "gender" : "female", "age" : 28, "salary" : 11000 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("59328cd6a7865327915046b0"), "name" : "Wentworth Earl Miller", "gender" : "male", "age" : 41, "salary" : 33000 }
降序
> db.user.find().sort({salary:-1})
{ "_id" : ObjectId("59328cd6a7865327915046b0"), "name" : "Wentworth Earl Miller", "gender" : "male", "age" : 41, "salary" : 33000 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("59328c8aa7865327915046ae"), "name" : "GalGadot", "gender" : "female", "age" : 28, "salary" : 11000 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("59328c9da7865327915046af"), "name" : "Mikie Hara", "gender" : "female", "age" : 26, "salary" : 7000 }
4.2.7 统计查询结果中记录的条数
(1)统计集合中的所有记录条数
> db.user.find().count()
3
(2)查询符合条件的记录数
查询 salary 小于 4000 或大于 10000 的记录数
> db.user.find({$or: [{salary: {$lt:4000}}, {salary: {$gt:10000}}]}).count()
2
4.3 删除操作
4.3.1 删除整个集合中的所有数据
> db.wangshibo.find()
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5932683b156e298477cdf3ad"), "name" : "菜鸟教程" }
> db.wangshibo.remove({})
WriteResult({ "nRemoved" : 1 })
> db.wangshibo.find()
>
可见 wangshibo中的记录全部被删除。
mongo在删除数据的时候不支持 all * 全部删除选择{}就可以全部删除了
删除mongodb集合中的数据可以使用remove()函数。remove()函数可以接受一个查询文档作为可选参数来有选择性的删除符合条件的文档。
remove()函数不会删除集合本身,同时,原有的索引也同样不会被删除。
删除文档是永久性的,不能撤销,也不能恢复的。因此,在执行remove()函数前先用find()命令来查看下是否正确,是个比较好的习惯啦。
注意 db.collection.remove()和 drop()的区别,remove()只是删除了集合中所有的记录, 而集合中原有的索引等信息还在,而
drop()则把集合相关信息整个删除(包括索引)。
4.3.2 删除集合中符合条件的所有记录
> db.user.find()
{ "_id" : ObjectId("59328c8aa7865327915046ae"), "name" : "GalGadot", "gender" : "female", "age" : 28, "salary" : 11000 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("59328c9da7865327915046af"), "name" : "Mikie Hara", "gender" : "female", "age" : 26, "salary" : 7000 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("59328cd6a7865327915046b0"), "name" : "Wentworth Earl Miller", "gender" : "male", "age" : 41, "salary" : 33000 }
> db.user.remove({name:'GalGadot'})
WriteResult({ "nRemoved" : 1 })
> db.user.find()
{ "_id" : ObjectId("59328c9da7865327915046af"), "name" : "Mikie Hara", "gender" : "female", "age" : 26, "salary" : 7000 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("59328cd6a7865327915046b0"), "name" : "Wentworth Earl Miller", "gender" : "male", "age" : 41, "salary" : 33000 }
4.3.3 删除集合中符合条件的一条记录
> db.user.find()
{ "_id" : ObjectId("59328c9da7865327915046af"), "name" : "Mikie Hara", "gender" : "female", "age" : 26, "salary" : 7000 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("59328cd6a7865327915046b0"), "name" : "Wentworth Earl Miller", "gender" : "male", "age" : 41, "salary" : 33000 }
> db.user.remove({salary :{$lt:30000}},1)
WriteResult({ "nRemoved" : 1 })
> db.user.find()
{ "_id" : ObjectId("59328cd6a7865327915046b0"), "name" : "Wentworth Earl Miller", "gender" : "male", "age" : 41, "salary" : 33000 }
>
当然,也可以是命令:db.user.remove({salary :{$lt:30000}},true),因为true和1是一个意思
4.4 更新操作
4.4.1 赋值更新
db.collection.update(criteria, objNew, upsert, multi )
criteria:update 的查询条件,类似 sql update 查询内 where 后面的
objNew:update 的对象和一些更新的操作符(如$,$inc...)等,也可以理解为 sql update 查询内 set 后面的。
upsert : 如果不存在 update 的记录,是否插入 objNew,true 为插入,默认是 false,不插 入。
multi : mongodb 默认是 false,只更新找到的第一条记录,如果这个参数为 true,就把按条 件查出来多条记录全部更新。
> db.user.find()
{ "_id" : ObjectId("59328cd6a7865327915046b0"), "name" : "Wentworth Earl Miller", "gender" : "male", "age" : 41, "salary" : 33000 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("593293e2a7865327915046b2"), "name" : "GalGadot", "gender" : "female", "age" : 28, "salary" : 11000 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("593293f0a7865327915046b3"), "name" : "Gasdfdst", "gender" : "female", "age" : 58, "salary" : 60000 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("59329401a7865327915046b4"), "name" : "huihui", "gender" : "female", "age" : 18, "salary" : 23100 }
> db.user.update({name:'huihui'},{$set:{age:23}},false,true)
WriteResult({ "nMatched" : 1, "nUpserted" : 0, "nModified" : 1 })
> db.user.find()
{ "_id" : ObjectId("59328cd6a7865327915046b0"), "name" : "Wentworth Earl Miller", "gender" : "male", "age" : 41, "salary" : 33000 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("593293e2a7865327915046b2"), "name" : "GalGadot", "gender" : "female", "age" : 28, "salary" : 11000 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("593293f0a7865327915046b3"), "name" : "Gasdfdst", "gender" : "female", "age" : 58, "salary" : 60000 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("59329401a7865327915046b4"), "name" : "huihui", "gender" : "female", "age" : 23, "salary" : 23100 }
> db.user.update({name:'lfqy1'},{$set:{age:23}},true,true)
WriteResult({
"nMatched" : 0,
"nUpserted" : 1,
"nModified" : 0,
"_id" : ObjectId("5932946c9758703fe04b0f73")
})
> db.user.find()
{ "_id" : ObjectId("59328cd6a7865327915046b0"), "name" : "Wentworth Earl Miller", "gender" : "male", "age" : 41, "salary" : 33000 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("593293e2a7865327915046b2"), "name" : "GalGadot", "gender" : "female", "age" : 28, "salary" : 11000 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("593293f0a7865327915046b3"), "name" : "Gasdfdst", "gender" : "female", "age" : 58, "salary" : 60000 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("59329401a7865327915046b4"), "name" : "huihui", "gender" : "female", "age" : 23, "salary" : 23100 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5932946c9758703fe04b0f73"), "name" : "lfqy1", "age" : 23 }
4.4.2 增值更新
> db.user.find()
{ "_id" : ObjectId("52453cfb25e437dfea8fd4f4"), "name" : "Gal Gadot", "gender" : "female", "age" : 28, "salary" : 11000 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("52453d8525e437dfea8fd4f5"), "name" : "Mikie Hara", "gender" : "female", "age" : 26, "salary" : 7000 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("52453e2125e437dfea8fd4f6"), "name" : "Wentworth Earl Miller", "gender" : "male", "age" : 41, "salary" : 33000 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("52454155d8947fb70d000000"), "name" : "not known", "sex_orientation" : "male", "age" : 13, "salary" : 30000 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5245610881c83a5bf26fc285"), "age" : 23, "name" : "lfqy1" }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("52455f8925e437dfea8fd4fd"), "age" : 23, "gender" : "male", "interest" : "NBA", "name" : "lfqy", "salary" : 1 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5245607525e437dfea8fd4fe"), "age" : 23, "gender" : "male", "interest" : "NBA", "name" : "lfqy", "salary" : 2 }
> db.user.update({gender:'female'},{$inc:{salary:50}},false,true)
> db.user.find()
{ "_id" : ObjectId("52453cfb25e437dfea8fd4f4"), "name" : "Gal Gadot", "gender" : "female", "age" : 28, "salary" : 11050 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("52453d8525e437dfea8fd4f5"), "name" : "Mikie Hara", "gender" : "female", "age" : 26, "salary" : 7050 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("52453e2125e437dfea8fd4f6"), "name" : "Wentworth Earl Miller", "gender" : "male", "age" : 41, "salary" : 33000 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("52454155d8947fb70d000000"), "name" : "not known", "sex_orientation" : "male", "age" : 13, "salary" : 30000 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5245610881c83a5bf26fc285"), "age" : 23, "name" : "lfqy1" }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("52455f8925e437dfea8fd4fd"), "age" : 23, "gender" : "male", "interest" : "NBA", "name" : "lfqy", "salary" : 1 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5245607525e437dfea8fd4fe"), "age" : 23, "gender" : "male", "interest" : "NBA", "name" : "lfqy", "salary" : 2 }
关于更新操作(db.collection.update(criteria, objNew, upsert, multi )),要说明的 是,如果 upsert 为 true,那么在没有找到符合更新条件的情况下,mongo 会在集合中插入 一条记录其值满足更新条件的记录(其中的字段只有更新条件中涉及的字段,字段的值满足 更新条件),然后将其更新(注意,如果更新条件是$lt 这种不等式条件,那么 upsert 插入
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
其它命令操作:
1、创建一个聚集集合(table)
db.createCollection(“collName”, {size: 20, capped: 5, max: 100});//创建成功会显示{“ok”:1}
//判断集合是否为定容量db.collName.isCapped();
2、得到指定名称的聚集集合(table)
db.getCollection("account");
3、得到当前db的所有聚集集合
db.getCollectionNames();
4、显示当前db所有聚集索引的状态
db.printCollectionStats();
三、用户相关
1、添加一个用户
db.addUser("name");
db.addUser("userName", "pwd123", true); 添加用户、设置密码、是否只读
2、数据库认证、安全模式
db.auth("userName", "123123");
3、显示当前所有用户
show users;
4、删除用户
db.removeUser("userName");
四、聚集集合查询
1、查询所有记录
db.userInfo.find();
相当于:select* from userInfo;
默认每页显示20条记录,当显示不下的情况下,可以用it迭代命令查询下一页数据。注意:键入it命令不能带“;”
但是你可以设置每页显示数据的大小,用DBQuery.shellBatchSize= 50;这样每页就显示50条记录了。
2、查询去掉后的当前聚集集合中的某列的重复数据
db.userInfo.distinct("name");
会过滤掉name中的相同数据
相当于:select distict name from userInfo;
3、查询age = 22的记录
db.userInfo.find({"age": 22});
相当于: select * from userInfo where age = 22;
4、查询age > 22的记录
db.userInfo.find({age: {$gt: 22}});
相当于:select * from userInfo where age >22;
5、查询age < 22的记录
db.userInfo.find({age: {$lt: 22}});
相当于:select * from userInfo where age <22;
6、查询age >= 25的记录
db.userInfo.find({age: {$gte: 25}});
相当于:select * from userInfo where age >= 25;
7、查询age <= 25的记录
db.userInfo.find({age: {$lte: 25}});
8、查询age >= 23 并且 age <= 26
db.userInfo.find({age: {$gte: 23, $lte: 26}});
9、查询name中包含 mongo的数据
db.userInfo.find({name: /mongo/});
//相当于%%
[code]select * from userInfo where name like ‘%mongo%';
10、查询name中以mongo开头的
db.userInfo.find({name: /^mongo/});
select * from userInfo where name like ‘mongo%';
11、查询指定列name、age数据
db.userInfo.find({}, {name: 1, age: 1});
相当于:select name, age from userInfo;
当然name也可以用true或false,当用ture的情况下河name:1效果一样,如果用false就是排除name,显示name以外的列信息。
12、查询指定列name、age数据, age > 25
db.userInfo.find({age: {$gt: 25}}, {name: 1, age: 1});
相当于:select name, age from userInfo where age >25;
13、按照年龄排序
升序:db.userInfo.find().sort({age: 1});
降序:db.userInfo.find().sort({age: -1});
14、查询name = zhangsan, age = 22的数据
db.userInfo.find({name: 'zhangsan', age: 22});
相当于:select * from userInfo where name = ‘zhangsan' and age = ‘22';
15、查询前5条数据
db.userInfo.find().limit(5);
相当于:selecttop 5 * from userInfo;
16、查询10条以后的数据
db.userInfo.find().skip(10);
相当于:select * from userInfo where id not in (
selecttop 10 * from userInfo
);
17、查询在5-10之间的数据
db.userInfo.find().limit(10).skip(5);
可用于分页,limit是pageSize,skip是第几页*pageSize
18、or与 查询
db.userInfo.find({$or: [{age: 22}, {age: 25}]});
相当于:select * from userInfo where age = 22 or age = 25;
19、查询第一条数据
db.userInfo.findOne();
相当于:selecttop 1 * from userInfo;
db.userInfo.find().limit(1);
20、查询某个结果集的记录条数
db.userInfo.find({age: {$gte: 25}}).count();
相当于:select count(*) from userInfo where age >= 20;
21、按照某列进行排序
db.userInfo.find({sex: {$exists: true}}).count();
相当于:select count(sex) from userInfo;
五、索引
1、创建索引
db.userInfo.ensureIndex({name: 1});
db.userInfo.ensureIndex({name: 1, ts: -1});
2、查询当前聚集集合所有索引
db.userInfo.getIndexes();
3、查看总索引记录大小
db.userInfo.totalIndexSize();
4、读取当前集合的所有index信息
db.users.reIndex();
5、删除指定索引
db.users.dropIndex("name_1");
6、删除所有索引索引
db.users.dropIndexes();
六、修改、添加、删除集合数据
1、添加
db.users.save({name: ‘zhangsan', age: 25, sex: true});
添加的数据的数据列,没有固定,根据添加的数据为准
2、修改
db.users.update({age: 25}, {$set: {name: 'changeName'}}, false, true);
相当于:update users set name = ‘changeName' where age = 25;
db.users.update({name: 'Lisi'}, {$inc: {age: 50}}, false, true);
相当于:update users set age = age + 50 where name = ‘Lisi';
db.users.update({name: 'Lisi'}, {$inc: {age: 50}, $set: {name: 'hoho'}}, false, true);
相当于:update users set age = age + 50, name = ‘hoho' where name = ‘Lisi';
3、删除
db.users.remove({age: 132});
4、查询修改删除
db.users.findAndModify({
query: {age: {$gte: 25}},
sort: {age: -1},
update: {$set: {name: 'a2'}, $inc: {age: 2}},
remove: true
});
db.runCommand({ findandmodify : "users",
query: {age: {$gte: 25}},
sort: {age: -1},
update: {$set: {name: 'a2'}, $inc: {age: 2}},
remove: true
});
update 或 remove 其中一个是必须的参数; 其他参数可选。
参数 详解 默认值
query 查询过滤条件 {}
sort 如果多个文档符合查询过滤条件,将以该参数指定的排列方式选择出排在首位的对象,该对象将被操作 {}
remove 若为true,被选中对象将在返回前被删除 N/A
update 一个 修改器对象
N/A
new 若为true,将返回修改后的对象而不是原始对象。在删除操作中,该参数被忽略。 false
fields 参见Retrieving a Subset of Fields (1.5.0+)
All fields
upsert 创建新对象若查询结果为空。 示例 (1.5.4+)
false
七、语句块操作
1、简单Hello World
print("Hello World!");
这种写法调用了print函数,和直接写入"Hello World!"的效果是一样的;
2、将一个对象转换成json
tojson(new Object());
tojson(new Object('a'));
3、循环添加数据
> for (var i = 0; i < 30; i++) {
... db.users.save({name: "u_" + i, age: 22 + i, sex: i % 2});
... };
这样就循环添加了30条数据,同样也可以省略括号的写法
> for (var i = 0; i < 30; i++) db.users.save({name: "u_" + i, age: 22 + i, sex: i % 2});
也是可以的,当你用db.users.find()查询的时候,显示多条数据而无法一页显示的情况下,可以用it查看下一页的信息;
4、find 游标查询
> var cursor = db.users.find();
> while (cursor.hasNext()) {
printjson(cursor.next());
}
这样就查询所有的users信息,同样可以这样写
var cursor = db.users.find();
while (cursor.hasNext()) { printjson(cursor.next); }
同样可以省略{}号
5、forEach迭代循环
db.users.find().forEach(printjson);
forEach中必须传递一个函数来处理每条迭代的数据信息
6、将find游标当数组处理
var cursor = db.users.find();
cursor[4];
取得下标索引为4的那条数据
既然可以当做数组处理,那么就可以获得它的长度:cursor.length();或者cursor.count();
那样我们也可以用循环显示数据
for (var i = 0, len = c.length(); i < len; i++) printjson(c[i]);
7、将find游标转换成数组
> var arr = db.users.find().toArray();
> printjson(arr[2]);
用toArray方法将其转换为数组
8、定制我们自己的查询结果
只显示age <= 28的并且只显示age这列数据
db.users.find({age: {$lte: 28}}, {age: 1}).forEach(printjson);
db.users.find({age: {$lte: 28}}, {age: true}).forEach(printjson);
排除age的列
db.users.find({age: {$lte: 28}}, {age: false}).forEach(printjson);
9、forEach传递函数显示信息
db.things.find({x:4}).forEach(function(x) {print(tojson(x));});
八、其他
1、查询之前的错误信息
db.getPrevError();
2、清除错误记录
db.resetError();
查看聚集集合基本信息
1、查看帮助 db.yourColl.help();
2、查询当前集合的数据条数 db.yourColl.count();
3、查看数据空间大小 db.userInfo.dataSize();
4、得到当前聚集集合所在的db db.userInfo.getDB();
5、得到当前聚集的状态 db.userInfo.stats();
6、得到聚集集合总大小 db.userInfo.totalSize();
7、聚集集合储存空间大小 db.userInfo.storageSize();
8、Shard版本信息 db.userInfo.getShardVersion()
9、聚集集合重命名 db.userInfo.renameCollection("users"); 将userInfo重命名为users
10、删除当前聚集集合 db.userInfo.drop();
show dbs:显示数据库列表
show collections:显示当前数据库中的集合(类似关系数据库中的表)
show users:显示用户
use <db name>:切换当前数据库,这和MS-SQL里面的意思一样
db.help():显示数据库操作命令,里面有很多的命令
db.foo.help():显示集合操作命令,同样有很多的命令,foo指的是当前数据库下,一个叫foo的集合,并非真正意义上的命令
db.foo.find():对于当前数据库中的foo集合进行数据查找(由于没有条件,会列出所有数据)
db.foo.find( { a : 1 } ):对于当前数据库中的foo集合进行查找,条件是数据中有一个属性叫a,且a的值为1
目录 返回
首页